I know what you might be thinking that why I am talking about chemical change when we are burning a candle. Yes, I have the same question floating in my mind. But trust me this is a really hot topic amongst all chemistry students and also the general public. The chemical change is one of the important terms of chemistry. But if you don’t know what chemical change actually is then it might be a little difficult for some of you. Yes, burning a candle is a chemical change because due to the burning of a candle carbon dioxide water vapors, heat, and light are released. Moreover, the change is irreversible as the initial substance cannot be recovered by any means. The loss or gain in energy and the irreversible nature of reaction are the characteristics of a chemical change. Therefore the burning of a candle is a chemical change. Let us learn more about what is a chemical change.
What is a Chemical Change?
A chemical change is usually an irreversible reaction that involves the rearrangement of one or more substances and change in their chemical properties or composition, resulting in the formation of at least one new product. When a substance combines with another substance or decomposes itself for the formation of new products, this is defined as the chemical change or also described as a chemical reaction. Such changes are irreversible and permanent, thus chemical changes cannot be reversed by changing or altering the experimental changes except by further chemical reactions. A chemical change is accompanied by a change in mass and energy. During a chemical change, the substance either gains or loses its mass. And also there is either loss or gain in energy due to the breaking of some bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in the product. Some examples of chemical change are, burning of wood or paper, souring of milk, burning of candles, digestion of food, and so on.
Chemical Change vs. Physical Change
A chemical change is the type of change wherein there are changes in the chemical properties of the matter whereas a physical change is one where the observable properties i.e. the physical properties of the matter changes. The physical change is accompanied by the change in the arrangement of molecules which leads to a change in state. No new products are formed, and also the composition of the matter remains totally the same. For example, in freezing water, the molecular composition of ice is the same as that of water. The chemical change is differentiated from the physical changes by the following points:
Why is Burning a Candle a Chemical Change?
The phenomenon of burning a candle is a chemical change because during burning the oxygen from the air reacts to form carbon dioxide. The formation of carbon dioxide which was earlier not present is evident in the fact that the burning of a candle is a chemical process. The burning of the candle is permanent because once it is burnt it cannot be recovered into the candle. A new product is also formed with a composition different from the candle. Hence it is a chemical change. Burning is a chemical process that occurs due to oxidation and thus produces heat and light. When a candle burns in the air, it combines with oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, and other gases due to which the mass of the product increases and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Why is Burning a Candle not a Physical Change?
The burning of a candle is not a physical change rather the melting of wax while the burning of a candle is a physical change. The burning of candles is accompanied by the formation of new products and the release of heat and light. For a reaction to be a physical change, there should not be the formation of any new products or release of energy but it is not the case on burning of a candle. Therefore, it proves that the burning of a candle is not a physical change. Though the burning of candles is not a physical change but melting of wax is a physical change. There is no change in the composition of wax when it melts down due to the burning of candles. The mass of wax before and after melting remains the same and on cooling down the wax solidifies as before. Therefore the change is reversible, hence the melting of wax is a physical change.
How Candle Works?
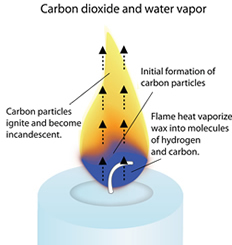
Candles are generally composed of hydrocarbons which include carbon and hydrogen. The burning of candles is powered by combustion. When the wick is lighted, the wax which gets melted is drawn up towards the wick through capillary action as the wick is a natural absorbent. The heat of the flame vaporizes the wax into gas and these gas molecules react with the oxygen from the air to form carbon dioxide, water vapors, and heat, and light. The wax acts as fuel during the entire reaction. CnH2n+1 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Heat + Light The heat released is responsible for more vaporization of the wax which is responsible for more combustion and formation of carbon dioxide, water vapors, and heat and light in more amounts. The combustion continues until the entire wax is consumed.
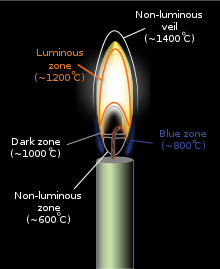
The flickering of flame or smoke while burning a candle at first may be observed because it takes some for the combustion to stabilize. The flame has four differently colored regions which describe various reactions occurring in the different regions. The blue colored innermost region is the oxygen-rich area where the hydrocarbons vapourize into carbon and hydrogen. Hydrogen is the first to react with air and form water vapors and a small amount of carbon burns to form carbon dioxide. The second layer is the brown layer where various other forms of carbon break down and settle and this region has relatively less oxygen content. The next layer is the yellow colored region where the formation of soot i.e. unburnt carbon increases. This is the most dominant region of a candle flame and therefore the human eye perceives the flame as yellow. The fourth and the outermost region of the flame is the blue edge which is the hottest region of the flame.
Check out the intersting video on how candles work.
Is Burning Candle Exothermic or Endothermic Reaction?
A reaction can be exothermic or endothermic based on whether the energy is released or gained. If a reaction releases energy in any form i.e. heat, light, etc. the reaction is said to be an exothermic reaction. In the case of exothermic reactions, the energy of products is always less than that of the reactants. An endothermic reaction is one in which energy is absorbed during the reaction, and hence the energy of the product is more than the energy of the reactants. The burning of a candle is an exothermic reaction as energy is released during the reaction in the form of heat and light. The exothermic nature of the reaction also describes that the amount of energy required to break the bonds in reactant molecules is less than the energy released during the formation of bonds in products.
Related Topic Is Burning Paper a chemical change Is Baking cake a chemical change Is Melting endothermic or exothermic
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that the burning of a candle is a chemical change as new products are formed. A chemical change is characterized by the formation of new substances, change in mass and energy of the substances, and the reaction is irreversible. The burning of a candle is accompanied by all these changes and thus it is a chemical change. These characteristics show that the burning of candles cannot be a physical change, but the melting of wax during the burning of a candle is a physical change. A candle burns on the principle of combustion in the presence of oxygen where due to capillary action the wax vaporizes to react with oxygen from the air to form carbon dioxide and water vapors. This reaction of the burning of a candle is an exothermic reaction as energy is released in the form of heat and light. The burning of a candle is thus a chemical change. Happy Reading!!
![]()